Introduction: A New Perspective on Risk Management
In the unpredictable realm of trading, managing risk is as crucial as chasing returns. While traders may rely on perpetual contracts or spot markets to capitalize on price movements, options provide a sophisticated layer of control. This article delves into the interplay of Bitcoin options and perpetual markets through a practical scenario. We’ll explore how options, particularly puts, in some circumstances can be used as a tool to hedge risk and secure gains, providing insights into their role in portfolio management.
A Scenario of Two Approaches
Bitcoin recently experienced significant price volatility, reaching all-time highs and then have been experiencing some fluctuations. Against such backdrop, two imaginary traders adopt distinct strategies to manage their exposure.
- Trader A: Engages in a straightforward long position in the Bitcoin perpetual market, banking entirely on price appreciation.
- Trader B: Mirrors Trader A’s position but integrates at-the-money put options into the strategy, adjusting them dynamically as the market evolves.
Both traders aim to maximize returns, but their contrasting approaches yield strikingly different outcomes.
Initial Setup
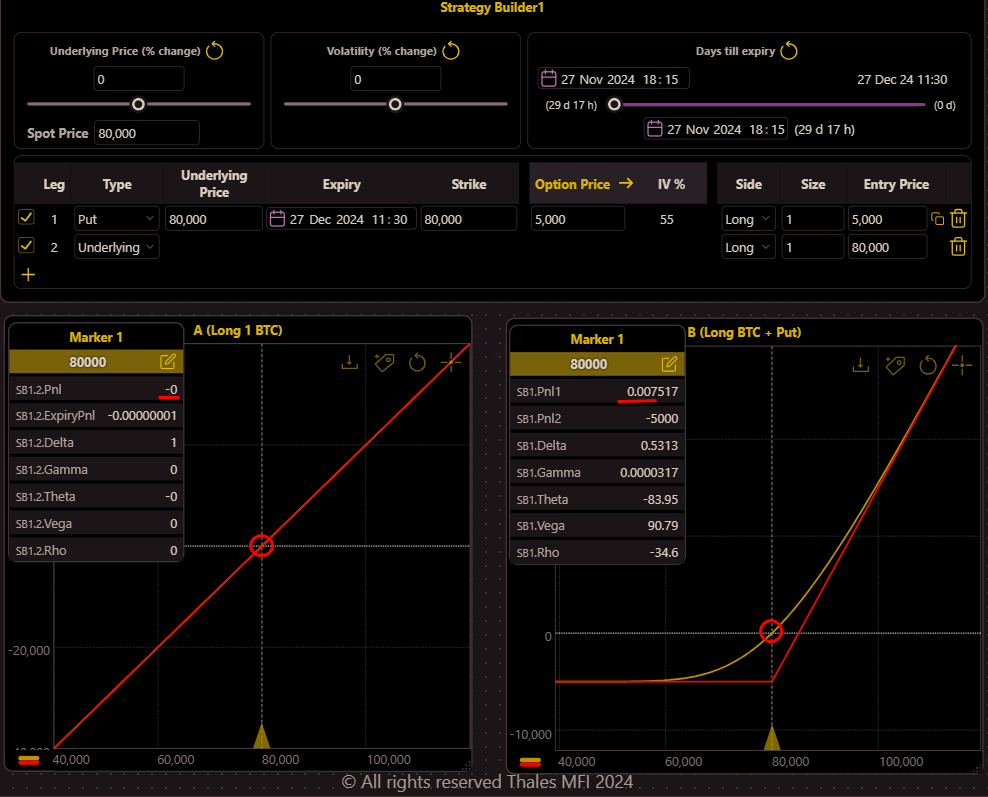
Let's consider Bitcoin's spot price to be $80,000. Using the Strategy Builder in Thales OSS, we simulate and compare two distinct trading strategies:
Trader A: Takes a pure long position in the perpetual market (row 2 in the Strategy Builder), fully exposed to Bitcoin's price movements without any protection (Left Graph)
Trader B: Mimics Trader A's long position but adds an $80,000 strike put option with a 30 DTE. This hedge introduces a cost (represented as negative PnL in the graph).
Bitcoin Rises Above $90,000
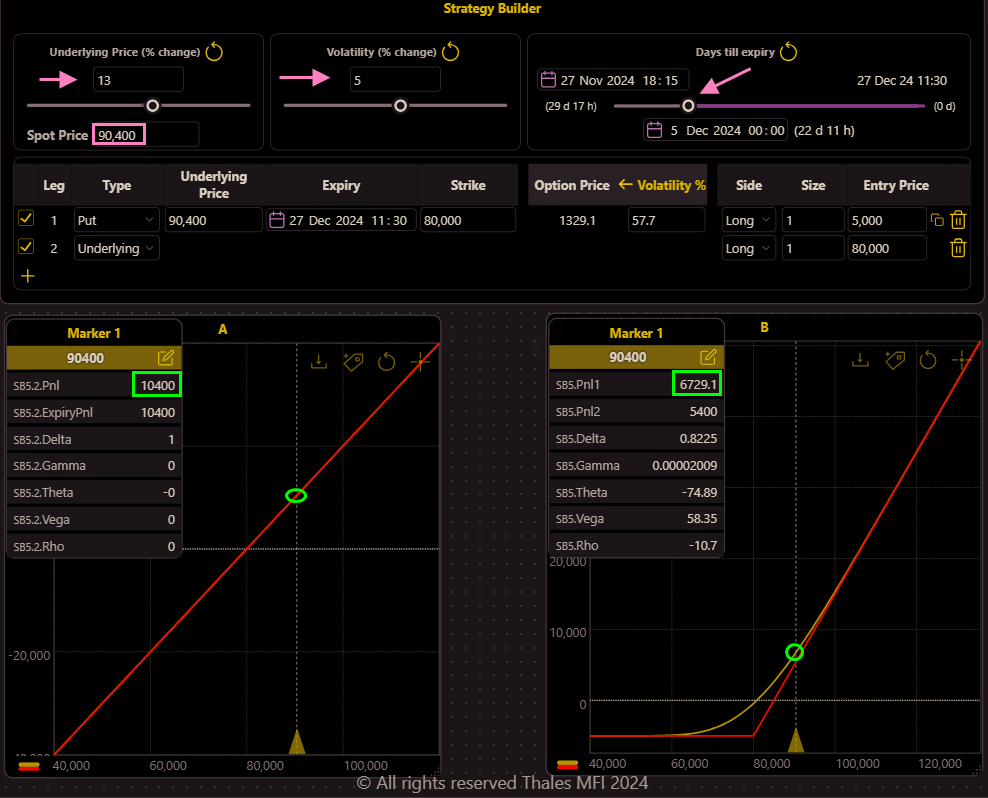
Let’s assume that Bitcoin’s price rises above $90,000, accompanied by a 5% increase in implied volatility (IV).
The updated graphs illustrate the impact of these conditions. While both Trader A and Trader B see gains from Bitcoin’s price appreciation, Trader B’s profile shows relatively lower profits. This difference arises from the premium paid for the protective put option, which slightly offsets the gains.
Rolling Up the Put Option: Adjusting Trader B's Strategy
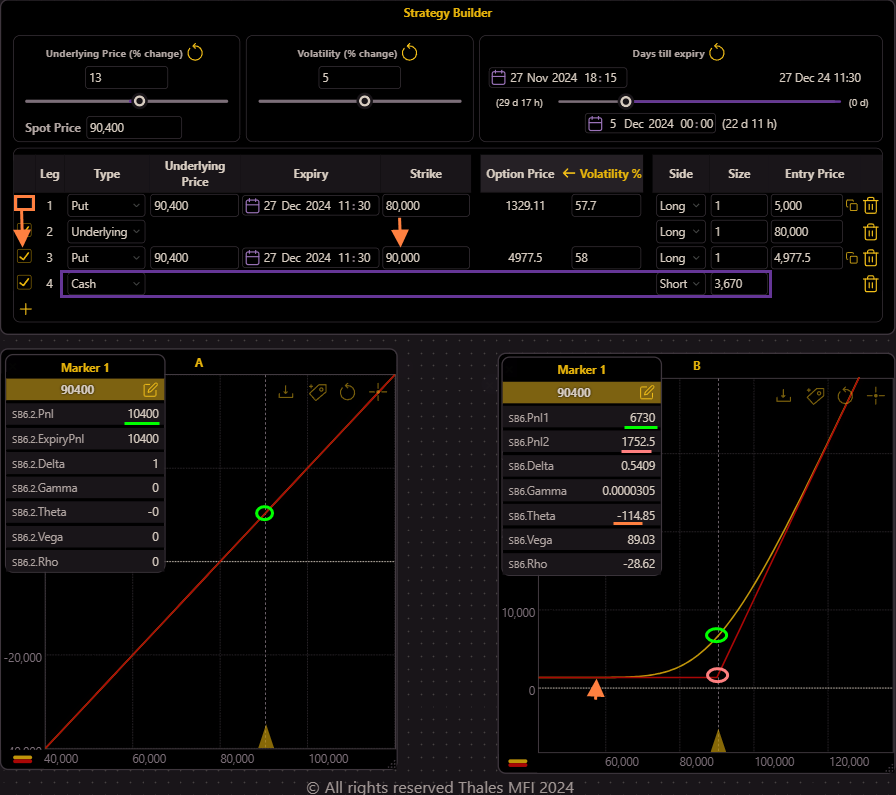
- Trader A: Enjoys the profit from the upward price movement and takes no further action, maintaining the pure long position in the perpetual market.
- Trader B: Adjusts the strategy by rolling up the put option to a higher, at-the-money (ATM) strike price while keeping the same expiry. This involves selling the previously purchased put option and buying a new one at the higher strike price. The rationale is to lock in more of the accumulated gains and provide better protection against future downside risks.
Implementing the Roll-Up in OSS: Using Thales OSS, we include the cash effects of this transaction in the simulation. By adding the cash leg, we account for the premium difference between selling the old put option before expiry and purchasing the higher strike put option. The impact is reflected in Graph B:
- Yellow Curve (Current PnL): The curve remains almost unchanged since the current value of the new put option is close to the premium difference, maintaining the current PnL.
Red Curve (PnL at Expiry): The red curve now stands totally above zero making sure that the strategy will never ends in loss.
Bitcoin Climbs Higher

Assuming the underlying price continues its upward trajectory as expected by both traders, Trader A demonstrates a stronger performance, benefiting more significantly from the price increase.
Another Roll-Up: Refining Trader B's Strategy

Trader A maintains their original strategy, benefiting from Bitcoin's continued price increase without any adjustments.
Trader B, on the other hand, rolls up their put option once again—this time from the $90,000 strike to the $98,000 strike, aiming to further lock in profits as the market moves upward.
Impact of the Roll-Up
- Cash Leg Adjustment: This roll-up incurs an additional cost, which is reflected in the cash leg. The difference in premiums between selling the $90,000 strike put and buying the $98,000 strike put is factored into the cash adjustment. It shows itself in the Theta as well.
Red Curve (PnL at Expiry): Despite the cost, the red curve on Graph B shows a significant upward shift, maintaining a clear positive area. This demonstrates that Trader B's rolling-up strategy continues to secure a higher floor for their position, ensuring their strategy remains profitable even under adverse conditions.
A Dramatic Turn: Bitcoin Collapses
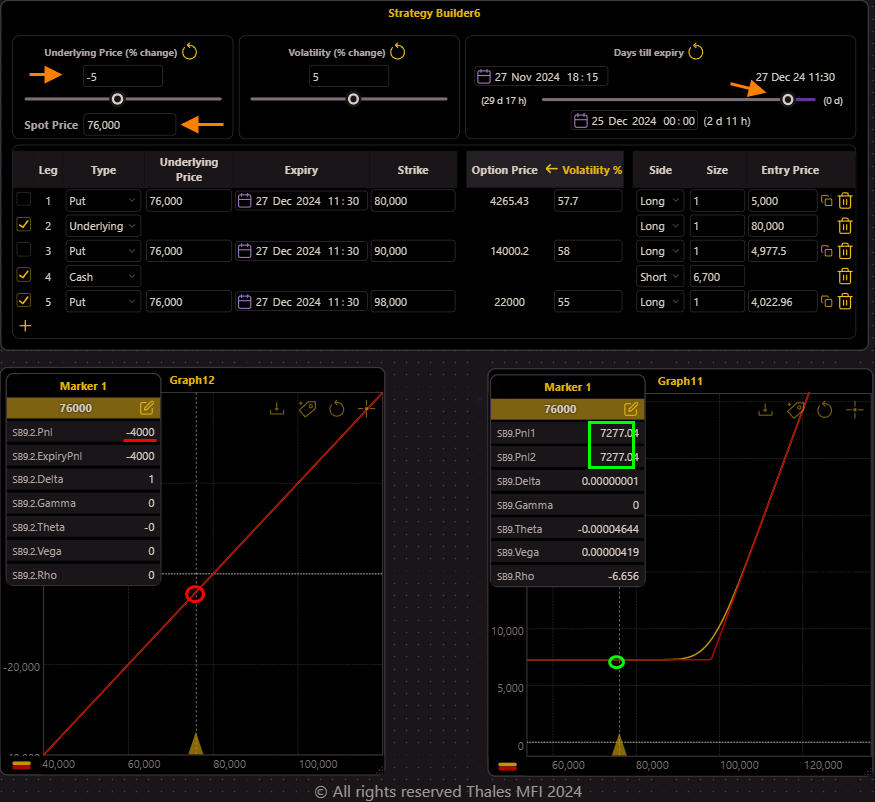
In this final scenario, we suppose a dramatic reversal in Bitcoin’s price. The underlying price plunges below its initial starting point, falling to $76,000.
Impact on Trader A:
- Losses Compound: Trader A, fully exposed to Bitcoin’s price movements without any protective hedge, suffers heavy losses. Their position dips significantly below zero, possibly even facing liquidation risk depending on leverage and collateral. What once seemed like an optimistic long trade has turned into a painful loss.
Impact on Trader B:
Calm Amid Chaos: Trader B’s foresight and use of options as a flexible risk management tool protect them from the sharp decline. Thanks to the rolling-up strategy, Trader B’s position remains firmly positive, harvesting the rewards of strategic adjustments made earlier in the trade
Bottom Line
Options as a Flexible Tool
This blog does not aim to establish one approach as superior. Instead, it highlights how options can serve as versatile instruments for traders to manage risk and control their portfolios more effectively. Trader B's strategy showcases just one of many methods to balance the potential upside of a market rally with protection against sudden downturns.
Risk Management in Perspective
Unlike stock or perpetual positions, which carry a delta of 1 and expose traders to both gains and losses with full intensity, options allow traders to hedge against the unexpected risks of volatile markets. In a bull market, while excitement surrounds potential price increases, the risk of corrections is ever-present. High volatility doesn't discriminate—it can drive prices in either direction, making risk management an essential component of any strategy.
Balanced Opportunities
By strategically rolling up puts, Trader B is able to lock in gains while retaining exposure to further upside. This approach demonstrates how options can provide a controlled mechanism to participate in a rally without leaving the portfolio entirely vulnerable to adverse price movements.
Empowered Decision-Making with Simulations
The simulations in Thales OSS emphasize the importance of visualizing and calculating risks and rewards. By adjusting variables like price, implied volatility (IV), and time passage, traders can explore different market scenarios and their potential impact. This empowers them to make well-informed, data-driven decisions tailored to their specific goals and risk tolerance.
Disclaimer
The content in this blog is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Options trading involves significant risk, and past performance is not indicative of future results. Always consult with a financial advisor before making investment decisions.